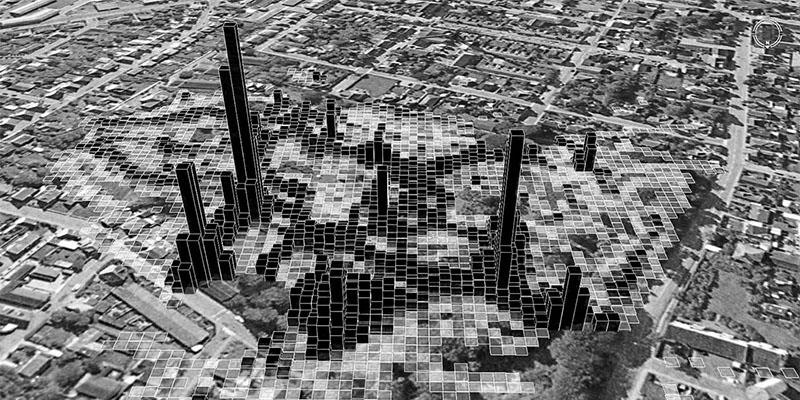
Tracking technologies such as GPS, mobile phone tracking, video and RFID monitoring are rapidly becoming part of daily life. Technological progress offers huge possibilities for studying human activity patterns in time and space in new ways. Delft University of Technology (TU Delft) held an international expert meeting in early 2007 to investigate the current and future possibilities and limitations of the application of tracking technologies in urban design and spatial planning. This book is the result of that expert meeting.
Urbanism on Track introduces the reader to the basics of tracking research and provides insight into its advantages above other research techniques. But it also shows the bottlenecks in gathering and processing data and applying research results to real-life problems. Urbanism on Track showcases tracking experiments in urban studies, planning and design – from pedestrian navigation in Austria to Danish field tests, from TU Delft's Spatial Metro project to MIT's Real Time Rome and last but not least the Sense of the City project realised in Eindhoven.
Urbanism on Track discusses the relevance of tracking for policy making, the possibilities of a new cartography and the implementation of tracking technologies in urban design and planning. This makes Urbanism on Track a unique book, setting the agenda for the structural embedment of research using tracking technologies in urbanism.
BOOK DATA
Publisher IOS Press // Book Editors Jeroen van Schaick, Stefan van der Spek, Frank van der Hoeven // Publication date December 2008 // Pages 200 // Duo-colour // ISBN 978-1586038175 // Price €70 / $99 Excl. VAT
Editorial
-
While the application of tracking technologies has developed substantially in social sciences and transportation sciences in the last decade, it has failed to make a significant impression in the scientific field of urbanism and spatial planning. The chair of Urban Design and the chair of spatial Planning at the Delft University of Technology noted this shortcoming while working within the framework of the EU-sponsored spatial metro project and the network cities research programme. In a joint effort, on 18 January 2007, they held an international expert meeting on the...
Articles
-
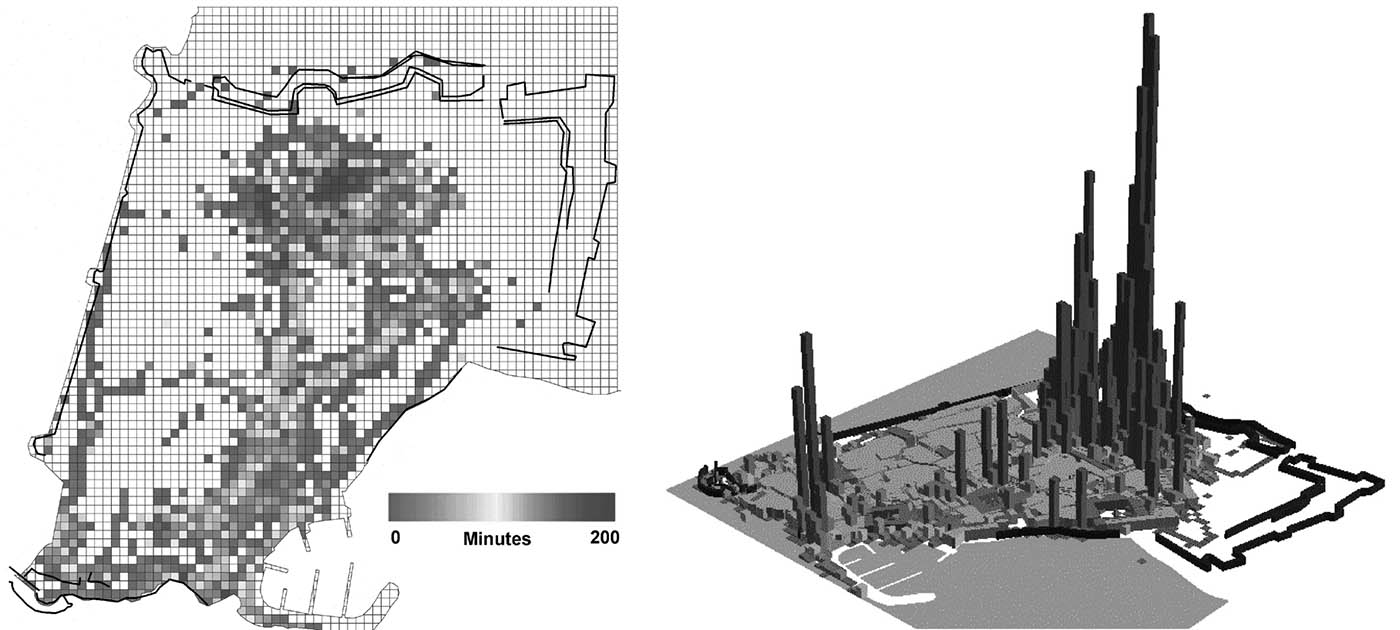
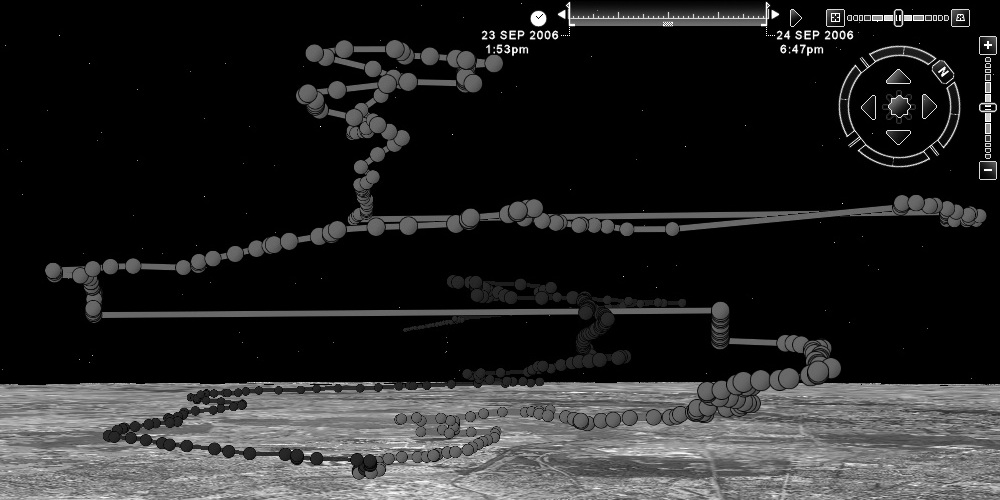
Shoval introduces us to the world of GPS tracking and presents two cases in which he used GPS-obtained data for his research on the outdoor mobility of elderly people with cognitive disorders and research on the user-density of an Israeli heritage site.
The first case relates to the sophistication of a location kit that is used to collect data for research focusing on the outdoor mobility of elderly people with cognitive disorders. This kit enables the researchers to measure not just the time-space activity of the research subjects, but also the level of their participation in the...
-
There is a growing demand for knowledge about processes in our cities, specifically the understanding of people's actual behaviour. Advanced Tracking Technologies offer the ability to give both actual and detailed insight into both people's individual and collective travel behaviour. The collected information can be used in urban analysis to map behaviour, feed prediction models, for simulation tools and for human behavioural sciences.
The use of emerging technologies such as GPS tracking, mobile phone tracking and RFiD is replacing existing methods and adding features to...
-
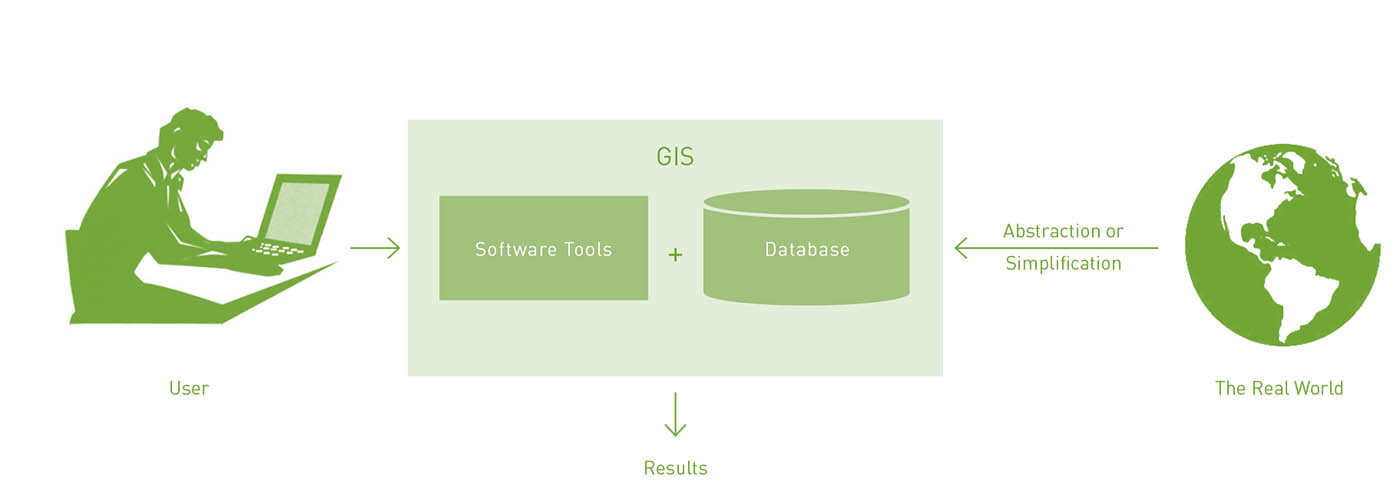
Urban planners and designers depend on spatial-oriented information and knowledge to comprehend a situation and to find design opportunities and solutions for spatial problems. Geographic location, spatial patterns and the distribution of features or events across an urban landscape inform many people of the decisions that planners either make or help others to make. as we will see in this chapter, a Geographic information system (GIS) provides urban planners with a platform on which they can deal with these complex spatial environments and represent, analyse and model them. It also...
-
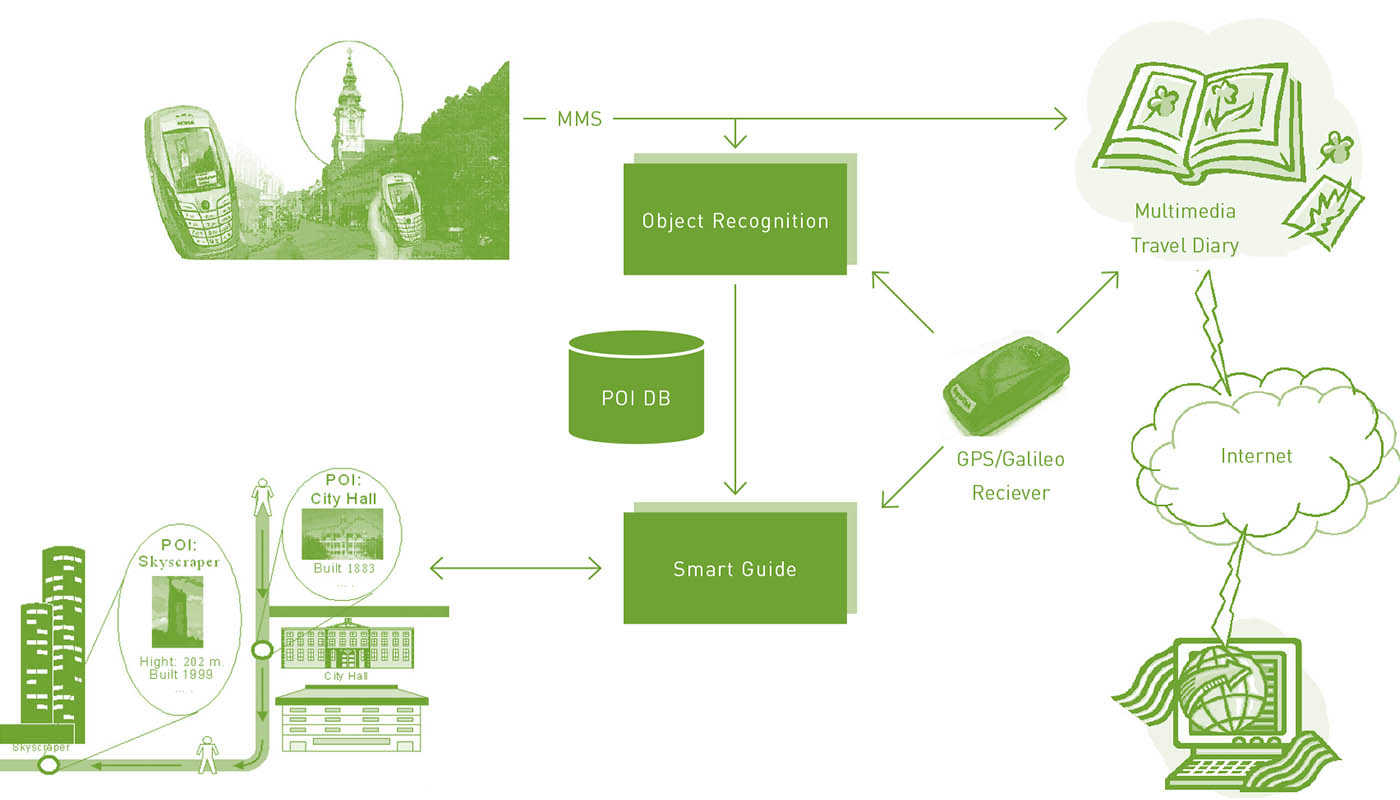
The first part of this paper gives a survey of the state of the art of research on human spatio-temporal behaviour in connection with the development of pedestrian navigation systems. The second part of the paper deals with the problem of pedestrian route choice behaviour. It is in particular concerned with localisation technologies and their adaptation to location-based information systems. The third part of the paper outlines three projects performed at arsenal research and the Vienna University of Technology in these areas. Firstly, it describes a research project on the requirements...
-
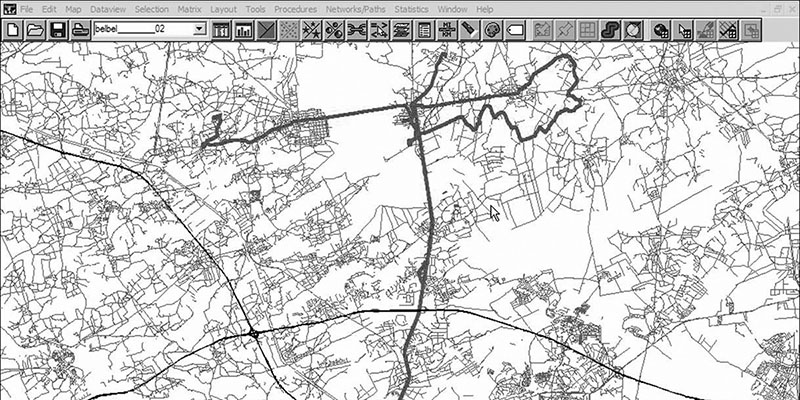
Very little scientific research based upon GPS tracking in a Danish context has been conducted and up until the present, no research at all has included comprehensive GPS tracking of human activity (cf. Jensen & Guldager, 2005; Jensen, 2003). There is therefore a need for explorative studies evaluating different tracking hardware and methodological set-ups and identifying various difficulties that may arise during data collection. From 2003 up to the present, the Diverse Urban Space (DUS) research project has conducted various experiments with the use of GPS tracking as a survey...
-
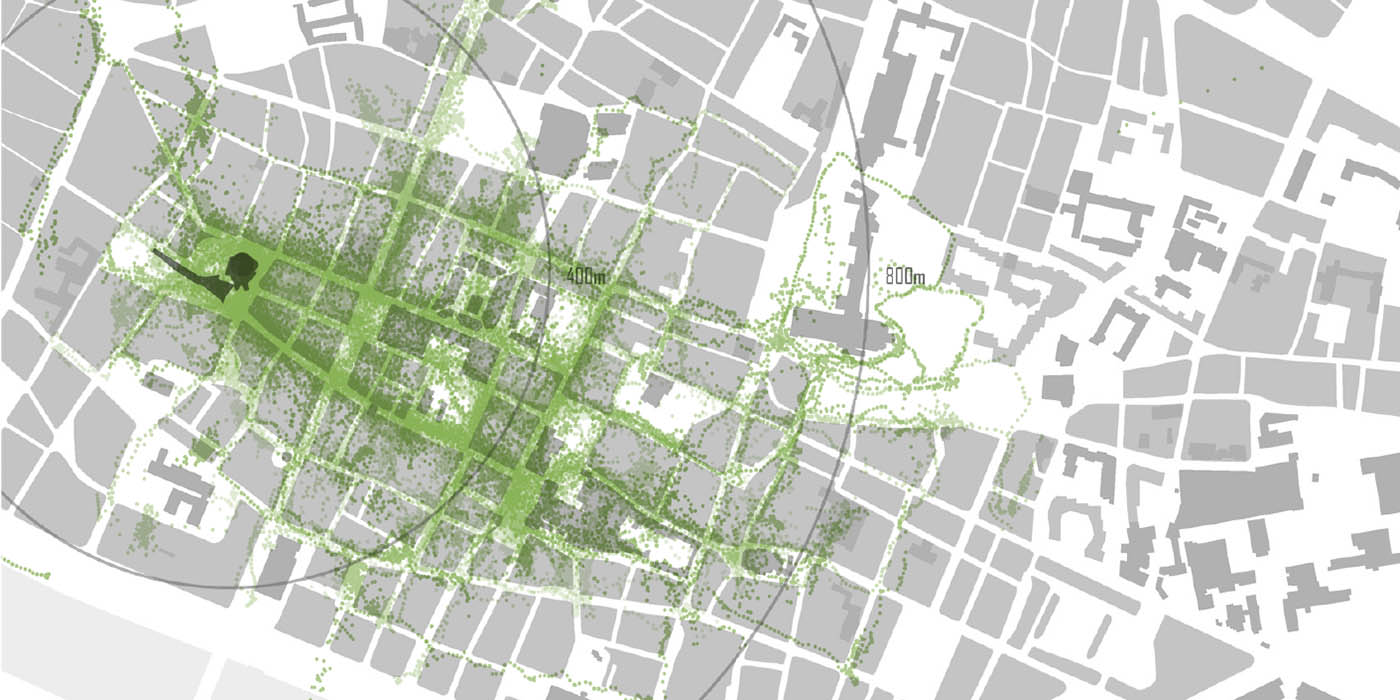
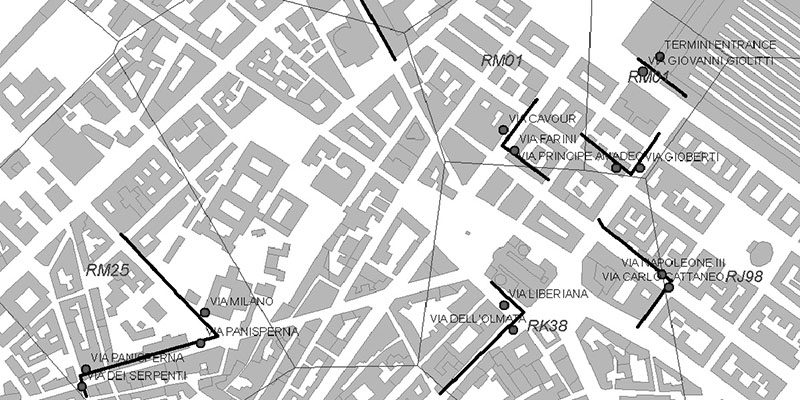
This chapter describes the results of a series of pedestrian observation studies carried out in Norwich, Rouen and Koblenz as part of the Spatial Metro project. The goal of these studies was to observe pedestrian behaviour and to investigate pedestrian movement and experience in the city centres. The cities are engaged in improving the physical conditions and the experience of their city centres by investing in landscaping and engineering of public spaces, city beautification, wayfinding and in communication and information technology.
The Spatial Metro project brings together a...
-
In recent years, a new approach for estimating people’s movement in cities has emerged through mobile phone positioning. As opposed to the more traditional methods of traffic surveys, automated counts, or individual counters on streets, the use of aggregated and anonymous cellular network log files has shown promise for large-scale surveys with notably smaller efforts and costs. In addition, a frequent data feed from the cellular network has also been argued to demonstrate fine grain over-time variation in urban movements, which are lacking from the traditional prediction methods....
-
Various applications of geo-referenced information currently being developed are or will be both commercially and publicly available. These applications combine functions such as mobile communication, GPS, digital photography, e-mail, cartography, satellite imaging and internet access. One of the first applications of so-called ‘location based services (LBS)’ has been the tracking & tracing of convicts on parole and animal species in the wild. In the United States, web-based products are available that enable parents to trace the whereabouts of their children, so-called child...
-
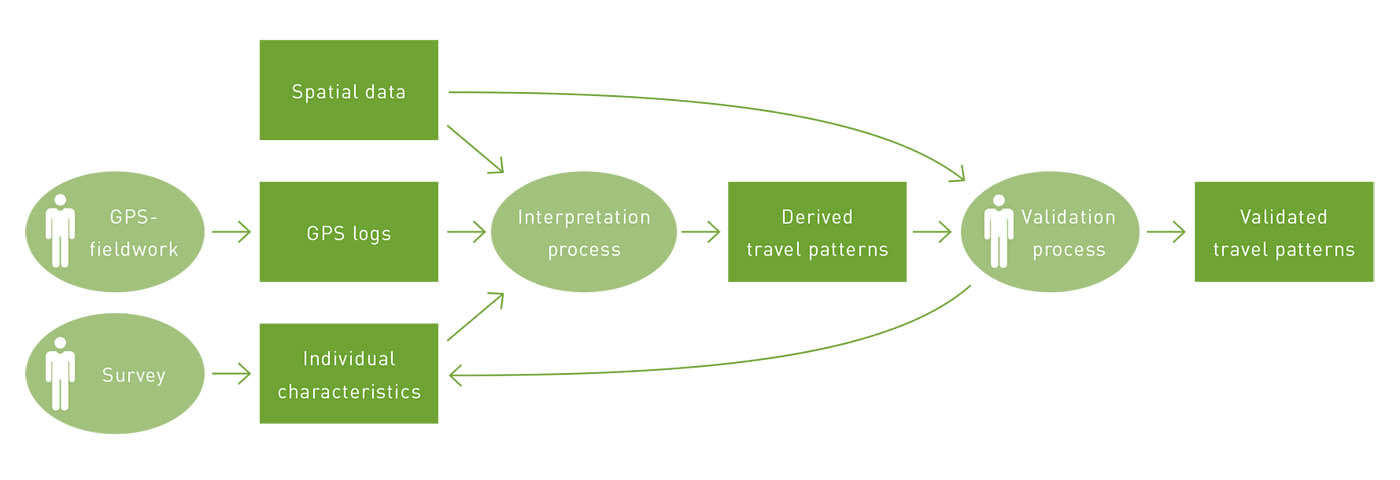
This chapter contributes to the improvement of GPS-based travel surveying by introducing a combined method of GPS, GIS and web-based user interaction, which has been applied in large- scale fieldwork in the netherlands. With over 1000 participants, as far as we know, this is the first time that a GPS-based method that measures travel mode choice as well as the location and type of destinations that are visited has been used on such a large scale. The chapter focuses in particular on the identification of travel modes and destinations, which is still an under-researched issue.
Our...
-
This chapter addresses two issues related to tracking people through mobile technologies and spatial planning decisions. The first major part deals with the question of how knowledge developed through the use of new tracking technologies can impact the spatial planning process. We argue that global positioning system (GPS) data are valuable – if not vital – for the improvement of travel demand forecasts by means of an activity-based transportation model when assessing travel demand management (TDM) policies such as spatial planning strategies.
Based on a brief historical outline...
-
In this chapter, we intend to present the map making state-of-the-art and discuss current and future prospects for the development of an automated methodology for map aggregation that takes into account the need for integration of mobility data and the social networking trend, which we believe will eventually become the main source of geographical maps. This will allow us to abstract a general architecture for a Collaborative Map Generation System and discuss in some detail the technical challenges for each module (and its current solutions).
In doing so, we hope to show that as a...
-
Van Schaick analyses the assumptions underlying the application of tracking technologies. On the basis of his findings and the results of the expert meeting Urbanism on track, he synthesises an agenda for the application of tracking research in the context of urban design and planning.